• Technology that provides increased storage functions and reliability through redundancy
• This is achieved by combining multiple disk drive component into a logical unit, where data is distributed across the drives in one of several ways called “RAID levels”
• RAID is now used as an umbrella term for computer data storage schemes that can divide and replicate data among multiple disk drives
• The schemes or architectures are named by the word RAID followed by a number (e.g. RAID 0, RAID 1)
• The various designs of RAID systems involve 2 key goals: increase data reliability and increase input/output performance
• When multiple physical disks are set up to use RAID technology, they are said to be in a RAID array
• This array distributes data across multiple disks, but the array is addressed by the operating system as one single disk
• RAID can be set up to serve several different purpose
Below is types of RAID
| Level | Description | Minimum # of disks | Space Efficiency | Fault Tolerance | Read Benefit | Write Benefit | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RAID 0 | Block-level striping without parity or mirroring. | 2 | 1 | 0 (none) | nX | nX |  |
| RAID 1 | Mirroring without parity or striping. | 2 | 1/n | n−1 disks | nX | 1X | 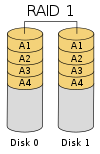 |
| RAID 2 | Bit-level striping with dedicated Hamming-code parity. | 3 | 1 − 1/n ⋅ log2(n-1) | RAID 2 can recover from 1 disk failure or repair corrupt data or parity when a corrupted bit's corresponding data and parity are good. |  | ||
| RAID 3 | Byte-level striping with dedicated parity. | 3 | 1 − 1/n | 1 disk |  | ||
| RAID 4 | Block-level striping with dedicated parity. | 3 | 1 − 1/n | 1 disk | 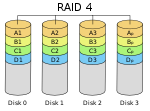 | ||
| RAID 5 | Block-level striping with distributed parity. | 3 | 1 − 1/n | 1 disk | (n−1)X | variable |  |
| RAID 6 | Block-level striping with double distributed parity. | 4 | 1 − 2/n | 2 disks |  |





0 comments:
Post a Comment