Chapter 3
Our class group Presentation + Quiz finally started during this week. Although our group haven't started do the presentation but it do make us nervous.
Somehow for the presentation of group The Destiny & Weconnectyou, they are doing their job with good. They do make their preparation and pass the knowledge to all of the student in the class.
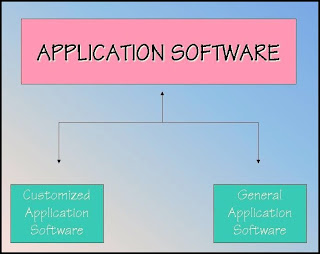
Application software
-Also known as an application or an "app"
-Is computer software designed to help the user to perform singular or multiple related specific tasks.
-It helps to solve problems in the real world.
-Contrasted with system software and middle ware
-Which manage and integrate a computer's capabilities, but typically do not directly apply them in the performance of tasks that benefit the user.
-A simple, if imperfect, analogy in the world of hardware would be the relationship of an electric light bulb (an application) to an electric power generation plant (a system).
-The power plant merely generates electricity, not itself of any real use until harnessed to an application like the electric light that performs a service that benefits the user.
-There are two categories of application software:
- Basic application
- Specialized application
Basic Application
-Are also called general-purpose
-There are some common types of basic application
- Word processors
- Spreadsheets
- Database management systems
- Presentation graphics
-More formally known as document preparation system
-Is a computer application used for the production (including composition, editing, formatting, and possibly printing) of any sort of printable material.
-May also refer to a type of stand-alone office machine
-Combining the keyboard text-entry and printing functions of an electric typewriter with a dedicated processor (like a computer processor) for the editing of text.
-Featured a monochrome display and the ability to save documents on memory cards or diskettes.
-Later models introduced innovations such as spell-checking programs, increased formatting options, and dot-matrix printing.
-As the more versatile combination of a personal computer and separate printer became commonplace.
-Most business-machine companies stopped manufacturing the word processor as a stand-alone office machine.
-As of 2009 there were only two U.S. companies, Classic and AlphaSmart, which still made stand-alone word processors.
-Many older machines, however, remain in use.
-Are descended from early text formatting tools (sometimes called text justification tools, from their only real capability).
-One of the earliest applications for the personal computer in office productivity.
-Although early word processors used tag-based markup for document formatting.
-Most modern word processors take advantage of a graphical user interface providing some form of what-you-see-is-what-you-get editing.
-Most are powerful systems consisting of one or more programs that can produce any arbitrary combination of images, graphics and text, the latter handled with type-setting capability.
-Microsoft Word is the most widely used word processing software.
-Many other word processing applications exist, including WordPerfect
-And open source applications OpenOffice.org Writer, AbiWord, KWord, and LyX.
-Web-based word processors, such as Google Docs, are a relatively new category.
General Features of word processor
-The clever people who design these programs have been very thorough.
-They have consulted professional publishers and discovered all the things that they want to be able to do with documents.
-And then they have programmed the software to make it do these things quickly and easily.
-To give one example - if you want to know the number of words in this document or any part of it, you can use the word count tool.
-It will count all the words in a document (default action) or just those in a passage you select.
Somehow these change over time, and are not exactly the same in all programs or all program versions.
The menu names or headings So what are these menu headings and what is in the menus? They are:
- File
- Edit
- View
- Insert
- Format
- Tools
- Table
- Window
- Help
The file menu
-You use this to start a new file. So what? Well do you accept the first document offered to you "blank document" or do you ever try out the other choices?
-These allow you to create a document based on a template.
An obvious point, but you can save on printing costs by using Print Preview until you are certain the document appears as you want it to.
Copy, cut and paste | Find | Search and replace
-This is one of the most creative of the sets of tools on the word processor.
-Use Copy to grab blocks of text, images, tables and other data objects
- Paste to place them in your document.
-This is a very useful tool for reading and research tasks.
-You can predict how often a given word or other text string occurs in a text.
-You can use this to find out which are the most common words or phrases.
-This is even more powerful, if you use it to find a given bit of text.
-You can replace this text with the SAME text, but in a different format.
Outline | Toolbars | The drawing toolbar
Outline -The View menu determines how the page looks on screen as you work.
-It does NOT affect the way the page will appear if you print it (use Print Preview for this).
-Most people have it set to Normal or Print Layout.
-But if you select Outline, you will find that you have lots of very useful tools for moving blocks of text.
Toolbar
-Your word processor has lots of toolbars.
-Usually you will see some but not all of these.
-The View menu allows you to display others.
-One of the most useful is the drawing toolbar.
-Use this to insert drawings, basic shapes, text boxes and callouts.
The Insert menu is good for putting images into your document, or things like page numbers and the date and time when the document was created. Practice putting these objects into your document:
- Picture
- Symbol
- Object
- Text box
- Auto shape
- Comment
The format menu
Font | Paragraph | Borders and shading
Once you have created a text or copied it from elsewhere, you can change its appearance to match the style you have chosen for your schoolwork. If you have a consistent house style, then your documents will look better together.
-This refers to the typeface or style.
-Professional typographers suggest that no more than two different fonts should appear on any page.
-Research shows that serif fonts are easier to read on a page, while sans serif fonts (such as Arial, which is used for this document) are easier to read on a computer monitor.
Times New Roman and serif fonts look like this.
-For emphasis you can use color, bold or italic.
-For another level of emphasis, you can use underlining.
-However, underlining on titles looks ugly - you won't see it on many professional publications.
-In writing Web pages, you should avoid underlining, as the browser uses this feature to show a hyperlink.
-You can set the style for paragraphs of various kinds, which show the structure of the document.
-For example, you can have a different style for each descending level in a hierarchy.
-Alternatively, you can keep the paragraph style the same, while using different levels of header, as in this document.
-You can set a range of borders and shading effects around different blocks or selections of text.
-This is a good way to make a selection stand out. But this works best if you use it sparingly.
You can set a range of borders and shading effects around different blocks or selections of text. This is a good way to make a selection stand out. But this works best if you use it sparingly. |
You can set a range of borders and shading effects around different blocks or selections of text. This is a good way to make a selection stand out. But this works best if you use it sparingly. |
The tools menu
Word count | Spelling and grammar | Options
-This is the most powerful selection of specialist tools for working on your document.
-You need to explore them in your own time, but you may want to pay attention to these.
You can get it to count all the words in a document, or in a selection.
-Use this intelligently.
-Make sure you set it to use the version of English you want - UK or International English rather than US English.
-We save the best for last.
You never need to use desktop publishing software for creating complex page layouts.
Changing format and style | Changing form or genre | Continuing texts
Changing format and style -Select the whole text or parts of it. Edit the text to make it look different. Do some of the following:
·
- change font (size, style, colour)
- change alignment (left, right, centre, justify)
- use highlighting or add a comment
- insert a picture
- use text boxes or callouts
-This means, for example, turning a passage of play dialogue into a novel or short story.
-Use a passage of text as a starting point. Continue the text, keeping the style consistent.
Substitutions | Grammar checking | Language change and spelling | Changing person and viewpoint | Undo and redo
-Create banks of words of different classes.
The witty young teacher thoughtfully wrote a silly sentence. |
-Then replace the colored words with other words of the same color (and category) from the table below:
Adjective | Adverb | Noun | Transitive verb |
big, little, happy, friendly, sad, unusual, ridiculous, blue, intelligent etc. | happily, rapidly, slowly, carefully, wisely, regularly, confidently, patiently, gently etc. | octopus, fish, anteater, teapot, motorbike, banana, football, roundabout, xylophone, fieldmouse, toilet, boy/girl/man/woman etc. | bit, kissed, touched, ate, cuddled, fondled, rode, struck, tortured etc. |
-With luck you will get surreal but grammatically sound sentences, like:
The toxic pink aardvark patiently fondled a drunken lifeboat. |
Grammar checking
-If your word processor has a grammar checker you can use this as a teaching/learning tool. The trick is to give them some text that contains non-standard forms to correct it.
Language change and spelling -You could also use this with regional or other varieties of English, such as pidgins.
Changing person and viewpoint -Use the Find and Replace tools to change the viewpoint in a text.
-Keep changing the passage until there are no mistakes in the grammar, and it makes sense when you read it aloud.
-The Undo and Redo functions are very powerful - and not just to remove a change you don't like.
-There are several ways to use the mouse or keyboard to control these tools - the most obvious is to click on the left and right pointing curly arrows on the toolbar (if you have this).
-Alternatively use the Edit menu, and choose the Undo or Redo options.
-Most convenient, if you can remember it, is to use the control Ctrl) key ( in combination with other letters on the keyboard - Control + z is Undo and Control + y is Redo.
References from 1. Computing Essentials Complete 2010 by Timothy J.O'Leary and Linda I.O'Leary from McGRAW Hill.
2. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Application_software
3. http://www.teachit.co.uk/armoore/resource/wordprocessor.htm